Sun Damage Prevention & Overheating this Summer
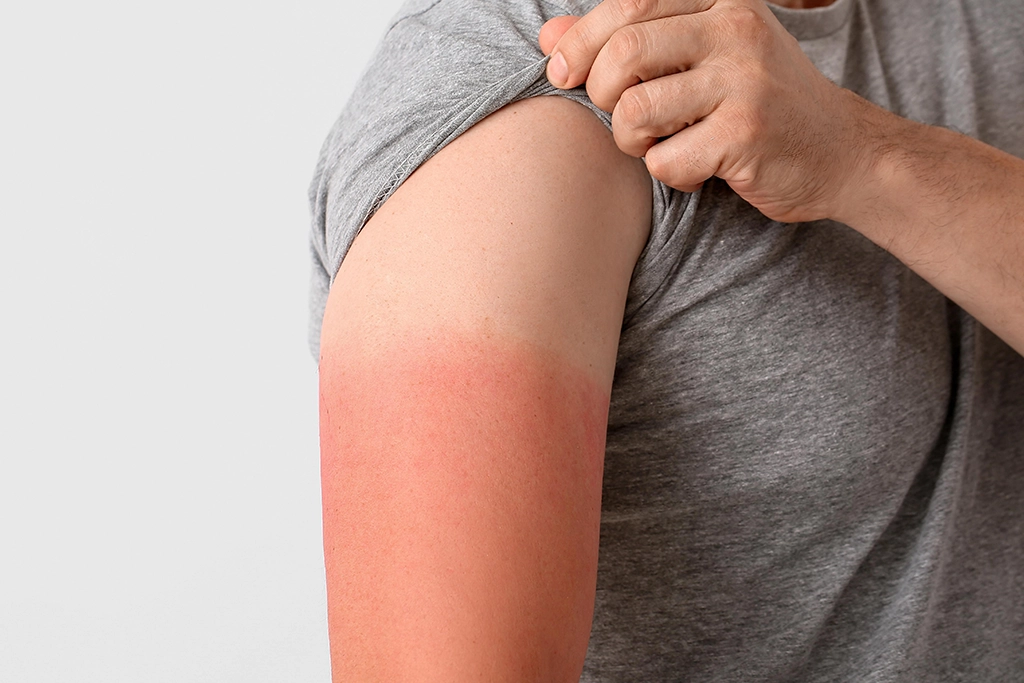
Sun Damage Prevention. Sun exposure is important for getting adequate amounts of vitamin D, but it can also be dangerous, cause skin damage, and overheating.
Even though frequent and long-term sun exposure can be harmful to everyone, it’s especially detrimental to the elderly, young kids, pregnant women, and those with chronic illnesses.
Sun Damage
Also called photoaging, sun damage occurs when the ultraviolet (UV) rays coming from the sun cause DNA changes on your skin on a cellular level. This shows up as premature aging as the damage causes loss of collagen, a stronger appearance of wrinkles, brown spots, broken capillaries, and uneven skin texture. And if all of this wasn’t enough, the DNA changes on the cellular level can very easily cause skin cancer.
Signs of sun damage start showing up as early as your twenties, drastically progressing as you age. Biologically, your skin loses collagen and ages as the years go by and sun damage only speeds the process.
Sunburns
Sunburns are an inflammatory reaction to UV rays and the damage they create to the outer layers of your skin. They can happen to anyone, but especially to those with lighter skin as they don’t have enough melanin to protect their cells. Sunburns can range from mild to severe and can be slightly red to bright red, swollen, and painful to the touch.
It’s important to note that you can get a sunburn even on an overcast day as the sun’s rays can easily penetrate through the clouds and cause damage to your skin.
Getting one sunburn might not seem so bad, but a repeated occurrence can cause long-term damage and consequences and cause a mutation in a tumor-suppressing gene, increasing the risk of developing cancer. Just five or more sunburns bring your risk of developing potentially deadly skin cancer (melanoma) to a dangerous degree. And studies show that most skin cancers occur among older generations of people.
How to Protect Yourself From Sun Damage?
Even though it’s important to spend some time in the sun and receive vitamin D, there are some tools you can use to protect yourself from the damaging UV rays. Here are some helpful tips:
- Use sunscreen every day – the UV rays can easily cause skin damage even through the clouds, so it’s important to use high sun protection factor every single day. And don’t forget about sunscreen for your face too!
- Wear protective clothing – Whether you’re just heading to the nearby grocery store or planning to be outside for an hour, it’s important to wear protective clothing to minimize the amount of exposed skin to the harmful sun rays. Wear long-sleeved, but breathable shirts and long pants, and always wear sunglasses and a hat.
- Choose the shade – even though it might feel nice to be hit by the sun’s warmth, it’s important to seek shade and spend more time away from direct sunlight. Sun safety is extremely important and if the person can’t take care of themselves, it’s important that their family members or caregiver ensures there’s shade, whether from a tree or a parasol.
- Schedule regular visits to your dermatologist – ideally, you should check your skin at least twice per year, especially after summer so your dermatologist can track your moles and other marks, ensuring to catch anything that might be developing as early as possible. On the other hand, self-checking should be performed on a monthly basis.
- Stay inside – when the weather is really extreme, it’s best to stay inside and protect yourself from sun damage by not even exposing your skin to it. Additionally, try to avoid spending time outside between noon and 5 pm when the sun’s rays hit the strongest.
- Stay hydrated – it goes without saying that optimal hydration is important for everyone, but seniors tend to lose more water through excessive perspiration so it’s important to replenish your water levels throughout the day.
Overheating
Another dangerous aspect of sun exposure and heat in the upcoming summer months is the risk of overheating. The risk of experiencing it grows as we age, and it’s really common in the senior population. The reasons for it are biological, but also lifestyle and health-related, as they’re more likely to develop a variety of chronic conditions or take medications that unable them from controlling and regulating their body temperature.
Symptoms of overheating include:
- Heat rash – on the skin, the rash appears as small blisters or a cluster of red bumps, mostly caused by excessive sweating. It usually shows up on the neck, chest, underarms, groin, or the back of your knees. Keep the areas dry and abstain from using any creams or ointments.
- Heat cramps – caused by loss of magnesium due to excessive sweating, muscle cramps and spasms can be really intense and painful. They usually show up in your abdomen, arms, and legs. The only real way to combat it is to stop doing whatever activity is causing strain, hydrate, take electrolytes, and see a doctor if the cramps become too intense or you have a history of heart disease.
- Heat syncope – A feeling of sudden dizziness, light-headedness, and weakness caused by prolonged sun exposure and dehydration. These factors can contribute to low blood pressure, so they can cause you to feel faint when getting up from a chair or suddenly switching planes. This increases the risk of injury or a fall, so make sure to always take your time when getting out of bed or from your seat, stay hydrated, and lie down if you feel dizzy. In extreme cases, a heat syncope can cause heat exhaustion and heat stroke.
- Heat exhaustion – occurs when your body is unable to cool itself and regulate its temperature. If left undealt with, it can progress to a heat stroke. The usual symptoms include pale and moist skin, excessive sweating, weakness, fatigue, muscle cramping, nausea, dizziness, shortness of breath, elevated heartbeat, and headaches. If you notice someone is experiencing these symptoms, help them move to a cooler location, take off their excessive clothing, put wet, cool cloths on their forehead and under their neck, and give them water to slowly sip on. If the symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention.
- Heat stroke – is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. The symptoms include an extremely high body temperature of 103F or more, nausea and vomiting, intense headaches, confusion and delirium, and even loss of consciousness. If left untreated, it can cause disability or death.
How to Prevent Overheating?
Some of the best ways to prevent overheating include:
- Stay inside if the weather is extremely hot and avoid heading outside between 12 and 5 pm
- Stay hydrated throughout the day and increase your water intake if you’ve spent more than one hour outside
- Dress in protective, but light, loose-fitting clothing so that it allows air to circulate
- Always wear a hat
- Abstain from intense physical activity that will cause excessive perspiration
- Wear broad-spectrum sunscreen all the time, even under clothing
Conclusion
Sun damage and overheating can cause serious complications that can be fatal if left untreated. It’s important to educate yourself on the symptoms of both and promptly react to the first warning signs. If you need additional resources, the Center for Disease Control (CDC), the National Institute on Aging, and Seniors Matter have some amazing tips and educational content you can access for free.


